GW Nanofabrication and Imaging Center
GW Nanofabrication and Imaging Center
Bridging Life Sciences and Materials Sciences Research
The George Washington University (GW) Nanofabrication and Imaging Center (GWNIC) features state-of-the-art microscopy instrumentation and a newly-constructed Class 100 cleanroom. GWNIC provides university-wide core infrastructure for research in engineering, chemistry, physics, biology, public health, medicine and biomedical sciences. Located at the heart of GW’s Foggy Bottom Campus, the GWNIC is a catalyst for cross-disciplinary collaboration.
Nanofabrication
GWNIC features ~5,000 sq ft of Class 100 cleanroom with major instrument clusters for lithography, deposition, etching, measurement and characterization.
Imaging
GWNIC comprises two imaging suites (~5,500 sq ft) with the latest light, confocal and electron microscopes. Sample preparation equipment and services are also available.
Featured Research
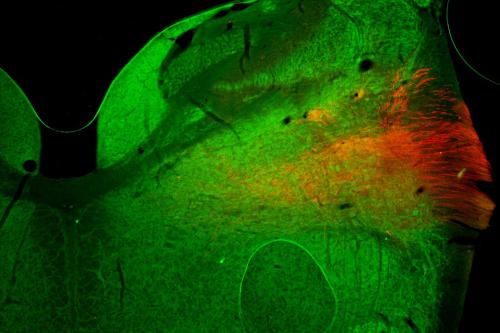
Study Reveals a Protein Called Snail May Play a Role in Healing Brain Injury
Researchers at the George Washington University discovered that a protein called Snail plays a key role in coordinating the response of brain cells after an injury. Read more in GW Today. Read the study, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Nexus.
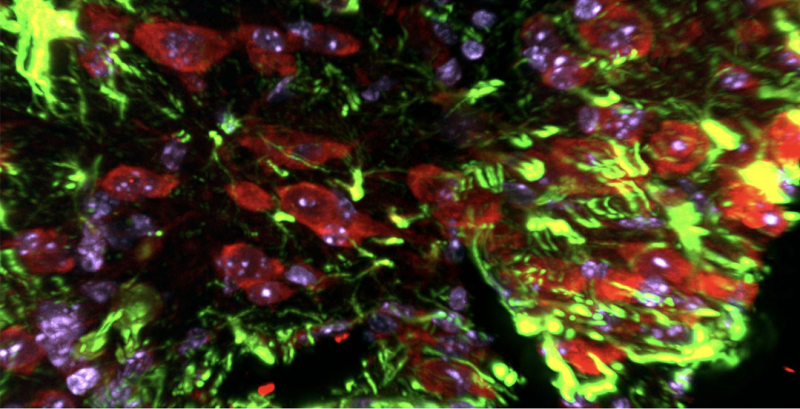
Segmentation performed on FIB-SEM images from corneas. Several individual axons are assigned different colors. One axon (aqua) moves in a different direction compared to the rest of the axons in the cluster shown. From Parlanti, P. et al., (2020), Axonal debris accumulates in corneal epithelial cells after intraepithelial corneal nerves are damaged: A focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM) study in Experimental Eye Research 194 (2020) 107998.
Segmentation performed on FIB-SEM images from corneas. Intraepithelial Corneal Basal Nerves (ICBNs) are assigned the color yellow and the corneal epithelial basement membrane is assigned the color purple. From Parlanti, P. et al., (2020), Axonal debris accumulates in corneal epithelial cells after intraepithelial corneal nerves are damaged: A focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM) study in Experimental Eye Research 194 (2020) 107998.